Have you ever wondered how a tire company can be associated with the world of haute cuisine? Today, we’re delving into the fascinating history of Michelin’s tire business and their unexpected connection to Michelin Stars.
Established in 1889, the French tire company Michelin is currently the world’s second-largest tire manufacturer, trailing only its rival Bridgestone of Japan. As of 2021, the company’s sales totalled approximately €23.8 billion, generating a net income of €1.8 billion.
Despite the fact that Michelin tires are used in Formula 1 race cars, luxury cars, and even space shuttles, the Michelin brand name does not immediately bring to mind the tire industry or the iconic Michelin Man. Rather, the brand is now widely associated with food.
The Michelin star system is an industry giant in its own right, with Michelin-starred chefs often regarded as culinary geniuses.
The Michelin Brothers
The Michelin tire company’s origins can be traced back to a fortuitous turn of events. When brothers Edouard and Andre assumed control of their father’s business, they were initially focused on manufacturing rubber-based farm equipment. Little did they know that their path would lead them to become pioneers in the world of tires.
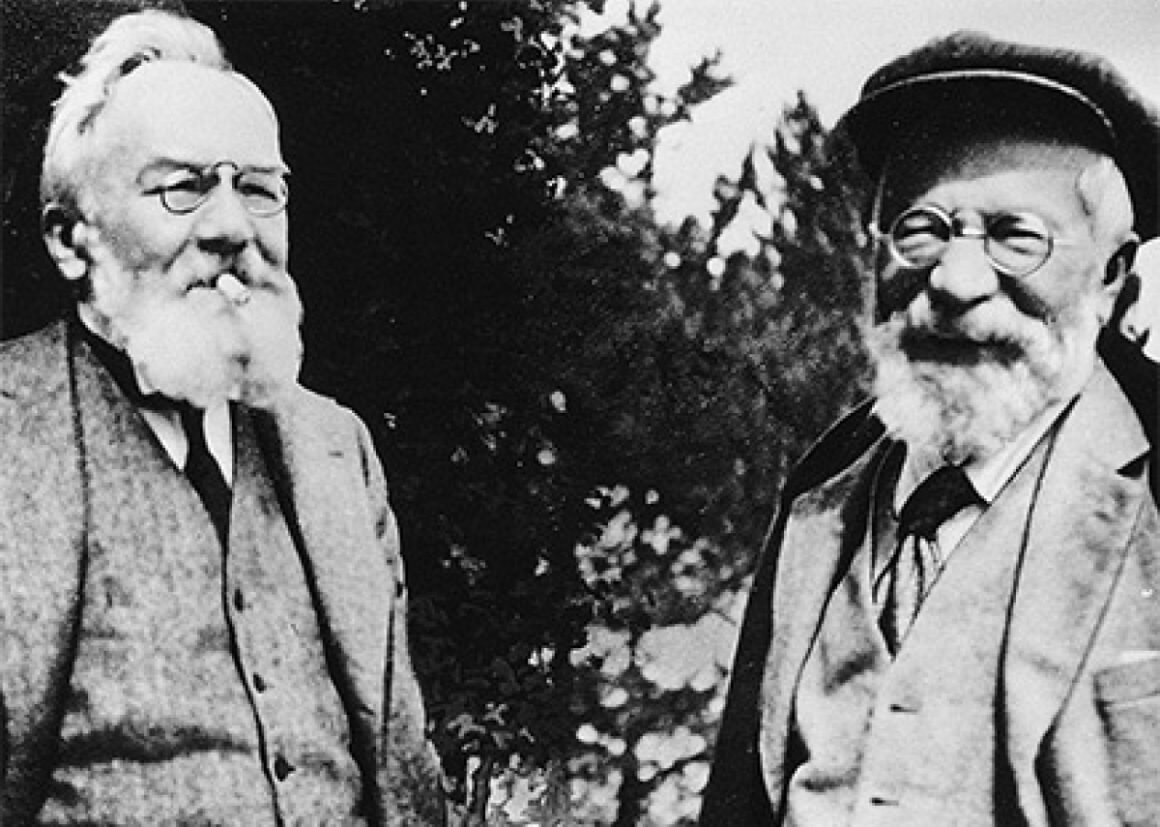

The Michelin brothers’ entry into the tire industry was sparked by a chance encounter with a cyclist who came to ask for their help in repairing his punctured tire. At the time, repairing a tire was a difficult and time-consuming process, prompting the brothers to explore alternative solutions. In 1891, they developed a revolutionary removable pneumatic tire, which marked the official entry of the Michelin brothers into the tire business.
The Michelin Guide Was Born
During the early 1900s in France, the demand for cars and frequent tire changes was relatively low, with only a little over 3,000 cars on the country’s roads, which posed a challenge for Michelin’s business prospects. To overcome this hurdle, Michelin not only had to convince existing car owners to choose their tires but also expand the market to attract more customers.
Recognising the popularity of travel guidebooks in 1900s France, they decided to create their very own guidebook. Thus, the inaugural Michelin Red Guide was published in 1900 and proved an instant success, selling an impressive 35,000 copies. This innovative guidebook featured maps, information on tire repair shops, maintenance tips, recommendations for mechanics, and more, all aimed at encouraging people to embark on travel adventures, preferably in their own vehicles. The copies of the Michelin Red Guide were enthusiastically purchased by aspiring car owners, particularly young individuals dreaming of owning a car someday!

Michelin recognized the passion that French people had for food and decided to incorporate independently reviewed restaurants in their travel guides. Since only the rich people could afford private vehicles, the guide’s aim was to associate Michelin with the most luxurious experiences in the country. Being featured in the Michelin guide became a status symbol for restaurants. In 1936, Michelin introduced the 3-star system to assign status. The strategy proved successful, as more restaurants in the guidebook meant more travel, and ultimately, more tyre sales for Michelin.
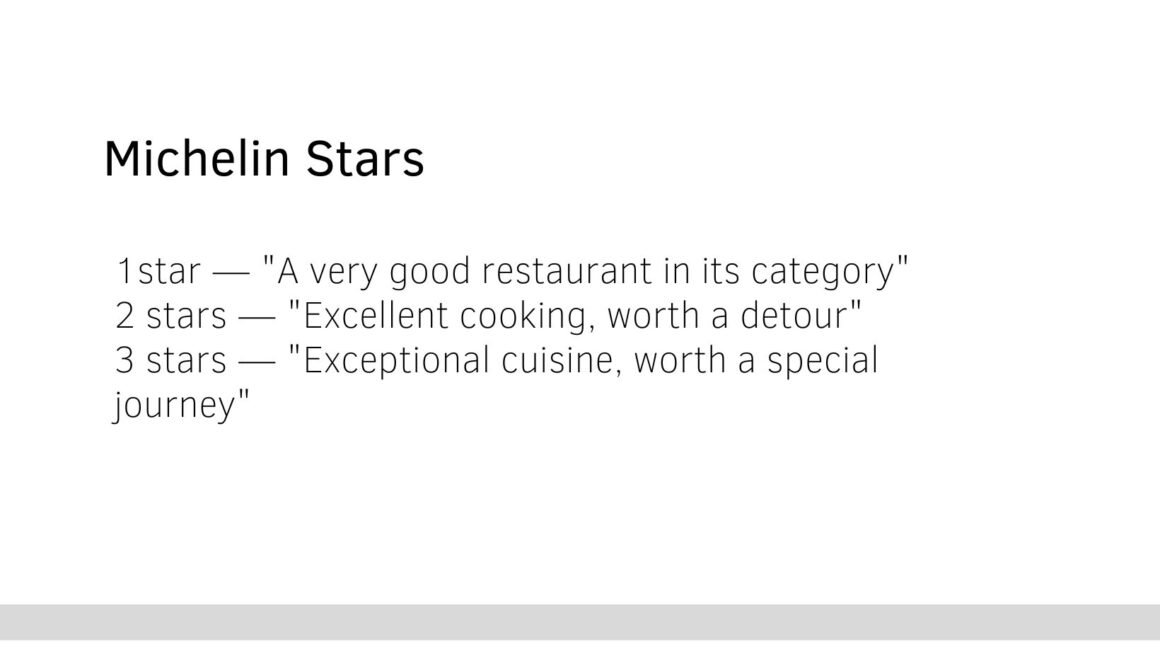
How Michelin Stars Are Awarded Today
Today, receiving a Michelin star is considered a great honor in the culinary world, and can have a significant impact on a restaurant’s reputation and success. Michelin inspectors, who are anonymous and highly trained food experts, visit restaurants multiple times and evaluate every aspect of the dining experience.
The evaluation process is thorough and rigorous, and includes a focus on the quality of the ingredients, the technique and skill of the kitchen, the creativity and originality of the cuisine, and the consistency of the food over time. Inspectors also consider factors such as the level of service, the wine list, and the ambiance of the restaurant.

Restaurants are not notified in advance of an inspection, and the identity of the inspector is never revealed. After the inspection, the inspector completes a detailed report, which is then reviewed by a team of experts. The decision to award a Michelin star (or multiple stars) is based on a consensus of these experts.
A Sign of Success
Receiving a Michelin star can have a profound impact on a restaurant’s business, as it can attract new customers, generate media attention, and help to establish a restaurant’s reputation as a leader in the culinary world. However, it’s important to note that the Michelin Guide is just one of many ways to evaluate a restaurant’s quality, and there are many excellent restaurants that do not have Michelin stars.

In recent years, the Michelin Guide has come under some criticism for being overly focused on traditional, high-end cuisine and for not sufficiently recognizing newer, more innovative restaurants. Nevertheless, the Michelin star remains one of the most prestigious and sought-after awards in the restaurant industry, and chefs and restaurant owners around the world continue to strive for the honor of receiving one.











